Shoulder injuries are among the most frequent setbacks that can sideline athletes at all levels of competition. This blog is designed to help you understand common shoulder injuries, their causes, and your recovery options.
Types of Common Shoulder Injuries
Common shoulder injuries for athletes include:
- Dislocations: When the upper arm bone pops out of the shoulder socket, often due to sudden impact or extreme rotation.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Damage to the group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint, often from repetitive overhead motions.
- Labral Tears: Injury to the cartilage rim surrounding the shoulder socket, which can result from acute trauma or repetitive stress.
- Shoulder Impingement: When tendons of the rotator cuff become irritated and inflamed as they pass through the shoulder joint.

Sports and Activities Prone to Shoulder Injuries
Certain sports and activities pose a higher risk for shoulder injuries due to their demanding nature on the joint. Some of these include:
- Baseball/Softball: The throwing motion puts significant stress on the shoulder, especially for pitchers.
- Swimming: The repetitive overhead arm movements can lead to overuse injuries.
- Tennis: Serving and overhead shots can strain the shoulder joint.
- Football: Tackles and falls can result in acute shoulder injuries.
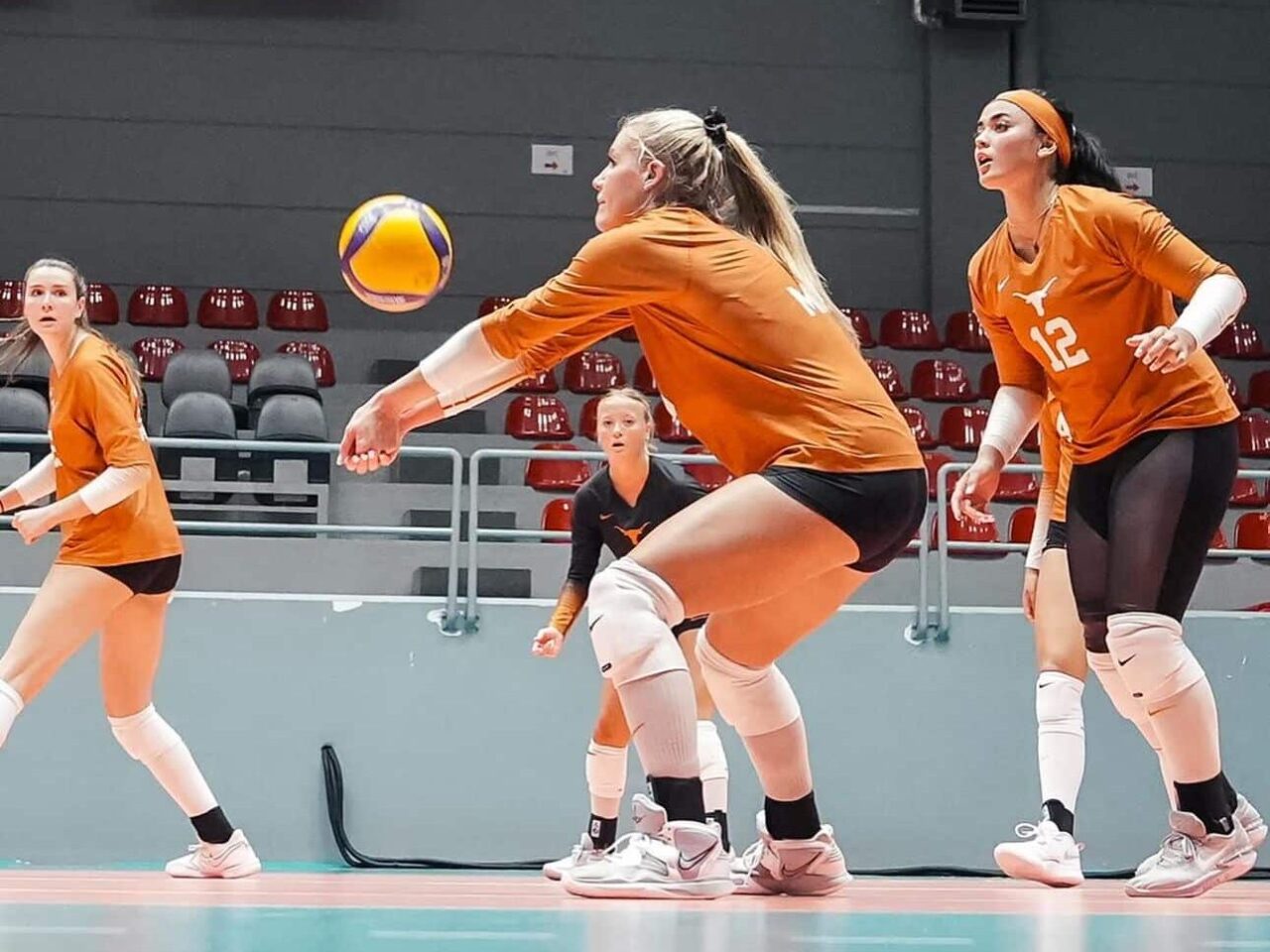
- Volleyball: Intense and repetitive overhead motions can lead to overuse injuries for blockers and hitters.
- Weightlifting: Improper form or excessive weight can lead to shoulder strain or injury.
“I recently got done with summer workouts, and I literally could not even lift my arm up above my head… I’m using my PowerPlay shoulder wrap basically every single day if my arm gets tight, and it feels so good.” Kenna Miller, Outside Hitter, University of Texas Volleyball
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Shoulder injuries often present with pain, limited range of motion, weakness, or a feeling of instability. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. This may involve a physical examination or imaging tests like X-rays or MRI.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment for shoulder injuries varies depending on the specific injury and its severity. Options may include:
- RICE: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation to reduce pain and swelling in the acute phase.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and stability are crucial for recovery.
- Immobilization: Using a sling to keep the shoulder still and protected during initial healing.
- Surgery: Some injuries, like severe rotator cuff tears or recurrent dislocations, may require surgical intervention.
Recovery timelines can range from a few weeks for minor injuries to several months for more severe cases.
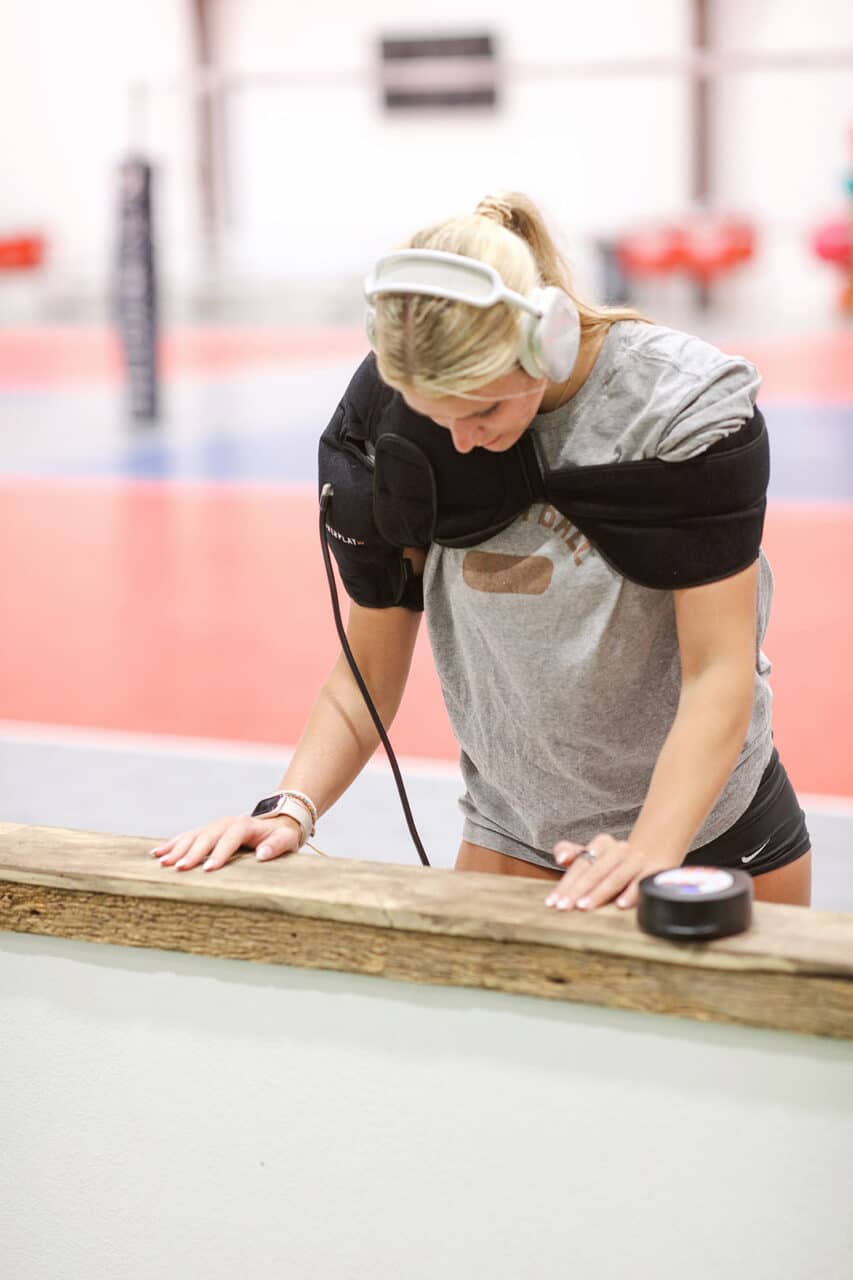
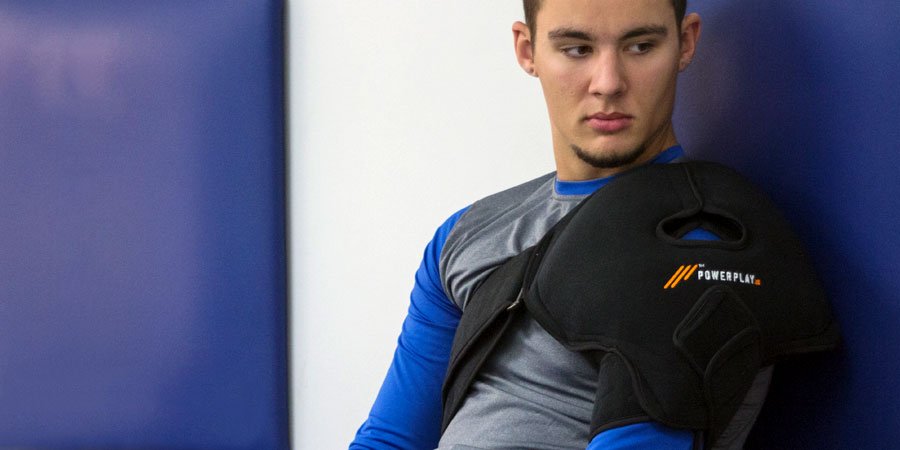
Cold Compression Therapy After Shoulder Injury
Cold compression therapy can be a valuable tool in treating shoulder injuries, especially in the initial stages after injury or surgery.
PowerPlay provides a specialized shoulder wrap that combines cold from an iceless gel pack with compression from a portable compression pump. The durable wrap uses several straps to provide a secure universal fit, delivering targeted cold and compression directly to the problem area.
Shop: PowerPlay’s Single Pack includes a pump, carry bag, and cold compression wrap of your choice.
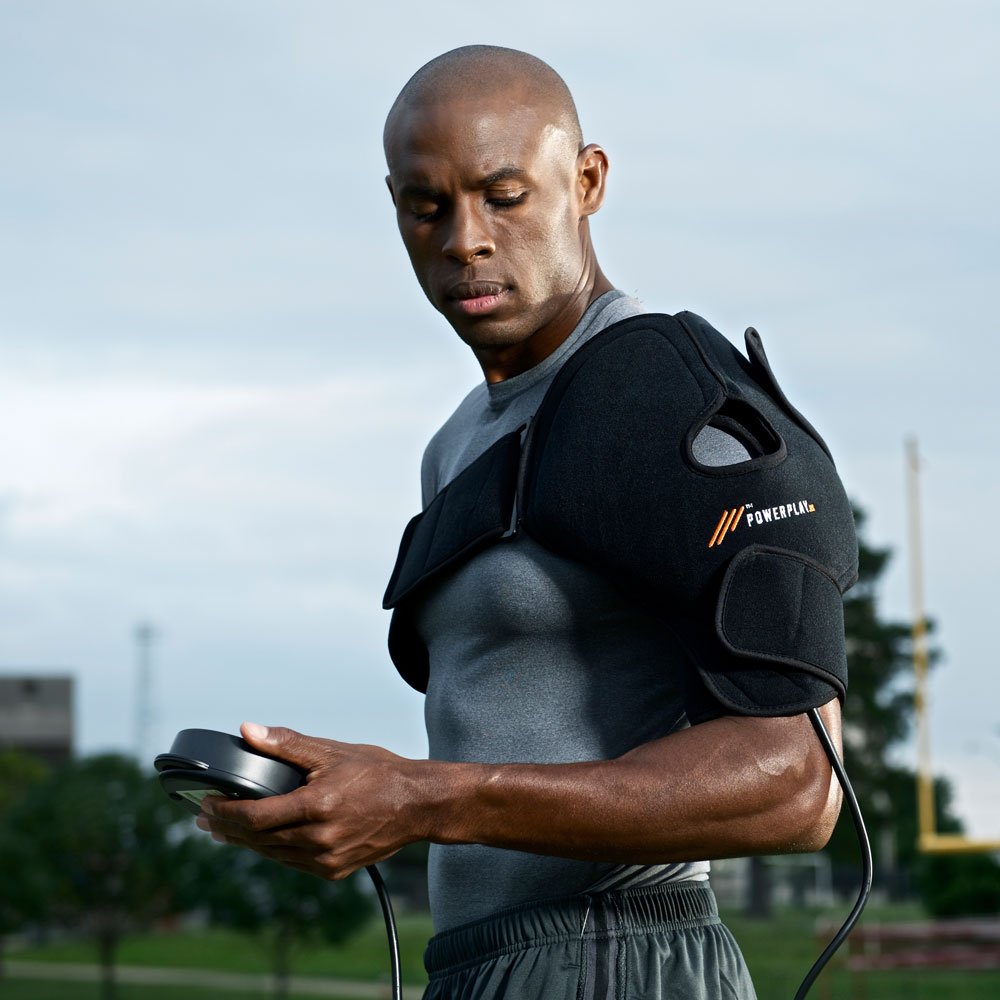

If you’re dealing with a shoulder injury, discuss with your healthcare provider whether cold compression therapy could benefit you. With proper treatment and rehabilitation, most athletes can return to their sports after a shoulder injury.
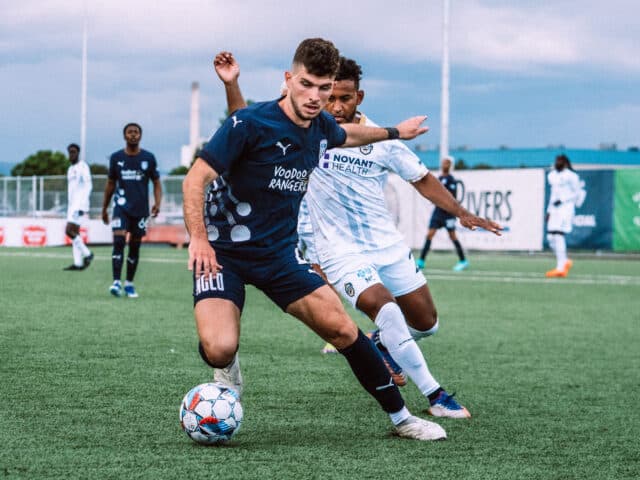
“PowerPlay has been easy to use during my recovery. I don’t have to worry about ice bags. The pump is small enough to fit in my pocket, so I can still move around. I’ve been able to avoid surgery because of PowerPlay.” Josh Cohen, Pro Soccer Player
Tips for Preventing Shoulder Injuries
To reduce the risk of shoulder injuries during sports or daily activities, physical therapists and athletic trainers often recommend:
- Proper Warm-Up: Always start with a dynamic warm-up routine to prepare your muscles and joints for physical activity.
- Strength Training: Focus on exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles to provide better support and stability.
- Proper Technique: Ensure you’re using correct form in your sport or activity, especially for repetitive motions like throwing or swimming.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of pain or discomfort in your shoulder and rest when needed to prevent overuse injuries.
- Maintain Flexibility: Incorporate stretching exercises into your routine to maintain flexibility in the muscles supporting your shoulder.
By being proactive about injury prevention and properly training and conditioning your shoulders, you can enjoy sports and activities while minimizing the risk of debilitating shoulder injuries. Before beginning athletic activities, consult with an athletic trainer or healthcare professional about your concerns.
“Start stretching now. Correct muscle imbalances by strengthening the weak muscle groups and stretching their muscle antagonists. If you’ve already moved into the injury zone, get help right away from a professional before a potentially short-term annoyance becomes a long-term problem.” Nicole Dorholt, Physical Therapist
Get Back in the Game with PowerPlay
Explore PowerPlay’s elbow wraps for effective cold compression therapy and faster recovery.
*The information featured on this page is subject to our standard content policy and disclaimer. It is available for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice.