Compression Therapy for Athletes
Training, conditioning, and competing take a toll even when an athlete is in tip-top shape. This is why it’s critical for athletes to figure out a rest and recovery routine in order to avoid injury.
Athletes & Recovery
Competing, intense workouts, and extra conditioning helps athletes stay in shape. However, compression therapy for athletes can help reduce injury risk.
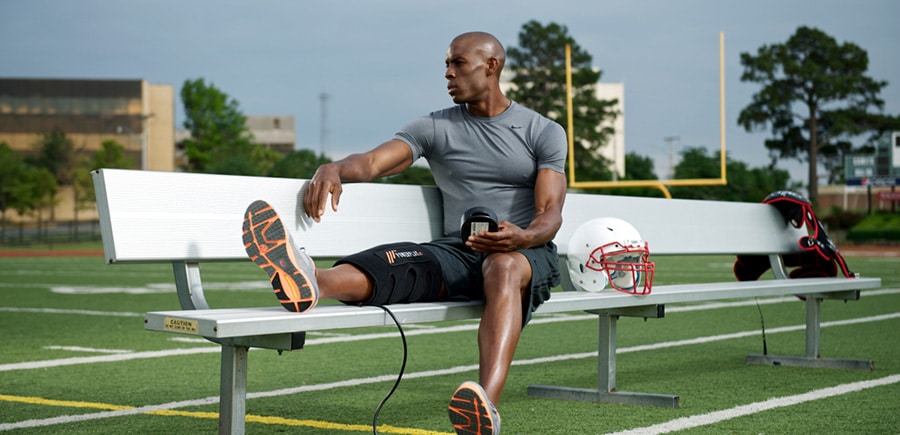

Common Injuries for Athletes
Benefits of Compression Therapy
Cold Therapy Machine
Athletic Recovery
Leg Compression Therapy
Athletic Injuries are Synonymous with Sports
It doesn’t matter if you are a collegiate athlete, a professional athlete, or a “weekend warrior.” Injuries are part of athletics.
Overexertion or hyperextensions are common when doing any repetitive motion. Other times, tired or weak joints can promote injury.
The most common athletic injuries include:
- Sprains: Not a particularly serious injury but extremely common, a sprain is the stretching or tearing of ligaments. While any ligament can be sprained, the most common location is the ankle. Mild sprains are treated at-home with rest, ice, compression, and elevation. However, severe sprains can require surgery in order to repair a torn ligament.
- Knee Injury: While knee injuries could include a variety of diagnoses, this joint is often injured during physical activity. Anything that interferes with how the knee joint moves while exercising can result in overstretching, or tearing muscles or tissues in the knee.
- Swollen muscles: While swelling is a natural reaction to help protect an injured part of the body, this can result in pain or discomfort.
- Achilles tendon rupture: Located on the back of the ankle, this thin tendon can break or rupture which leads to severe pain.
- Fracture: Broken bones are most common in sports such as football, basketball, and rugby. Marathon runners can also run into stress fractures if they’re not careful.
- Dislocations: A dislocation happens when a bone is forced out of its socket, symptoms for this injury include pain and swelling.
Overuse, unbalanced training, and improper rehabilitation often leads to these common injuries among athletes. However, athletes can take charge of their recovery and work to prevent injury.
Learn more about common injuries for athletes.
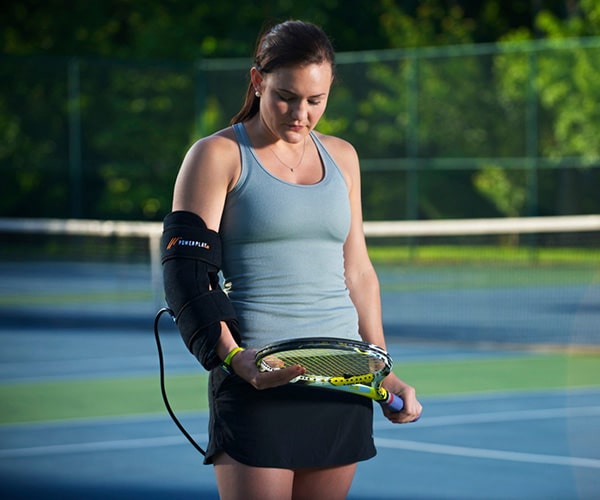
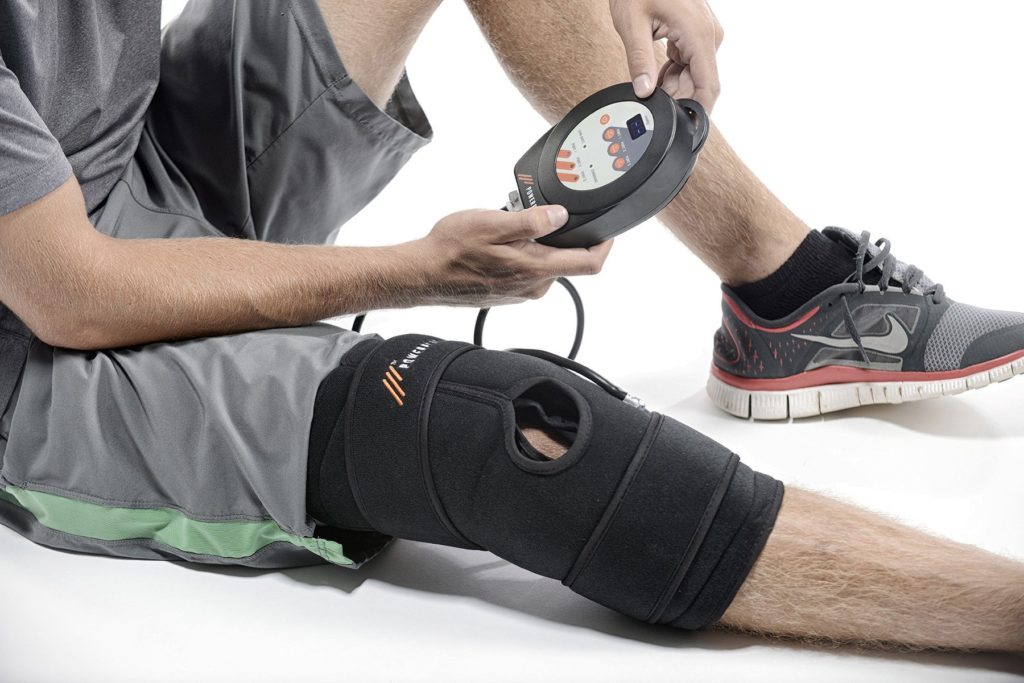


Benefits of Compression Therapy
If you’re training and competing with risk of injury, you can take measures that will prevent injury and promote recovery. By implementing a well-rounded fitness plan with elements of strength, cardio, and flexibility training along with your main sport, you will decrease your risk of injury. Also, taking the time to stretch and rest between workouts or training sessions will help your body recover, reducing injury risk.
Many athletes are adding compression therapy to their recovery routine. Compression therapy applies a “squeeze and release” method to a muscle group. Repetitive compression helps reduce swelling and repair tissue damage because it increases blood flow to specific parts of the body.
It’s suggested that athletes of any age apply compression therapy for 10-30 minutes after a workout or training exercise to quickly deliver oxygen to muscle cells. In theory, this aids in athletic endurance and increases performance.
Learn more about how to reduce swelling.
But reducing swelling is just one of several benefits of compression therapy for athletes. Other benefits include:
- Flushing lymphatic fluids and lactic acids which can cause pain
- Improving circulation
- Decreased recovery time
- Prevent muscle soreness
- Pain relief
- Increases flexibility
- Decreases fatigue
Cold Therapy
Another way to recover is to use a cold therapy machine or cryotherapy. The science and benefits behind cold therapy are similar to compression therapy. In a nutshell, cryotherapy aids in muscle soreness and decreases swelling.
Cold therapy restricts blood vessels, which decreases blood flow and thereby decreases muscle spasms, inflammation, soreness, and cramps.
While cold therapy provides great recovery benefits for athletes, it also has its drawbacks. For example, ice baths are only an option at home or in a hotel. While in a stadium setting, it’s easy to locate ice to apply an ice pack to an injured area. But for athletes on the road or at a gym, ice isn’t always convenient.
This is why gel packs are a great solution to cryotherapy. They don’t require water or ice, which is messy, and they allow athletes to use cold therapy from practically anywhere.
Learn more about how cold therapy helps alleviate pain.
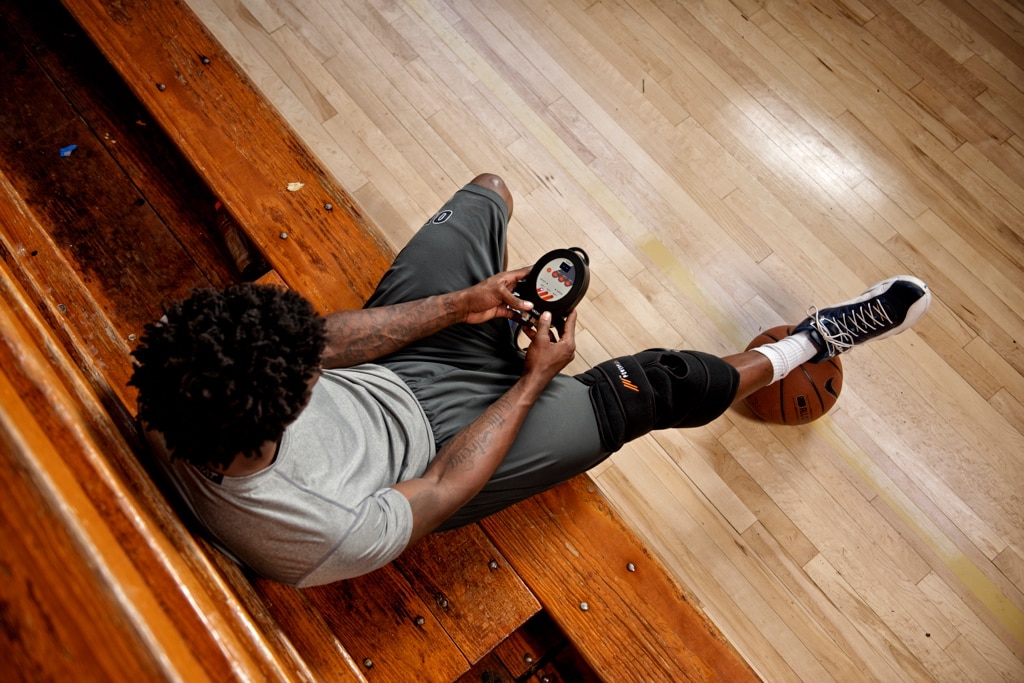
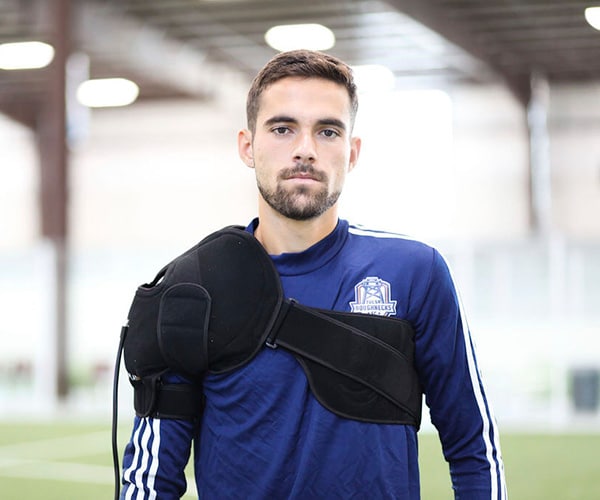


Athletic Recovery
Cold and compression therapy work well for recovery separately; however, combining the two methods together has further benefits. Studies find that when active compression is coupled with cold therapy, it results in increased blood flow, and decreased swelling, edema, and muscle spasms. Applying ice or cold to your injury also makes recovery less painful and more comfortable.
But of course, cold compression therapy isn’t the only way athletes can recover between workouts. Hydration is a main tool used to help athletes to recover, since dehydration causes muscles to not repair themselves. Aim for 16 to 24 ounces of fluid per pound during a training session, according to The American College of Sports Medicine.
Foods also play a role in athletic recovery. Eating healthy foods allows athletes to get the nutrients they need. In addition, minimize processed foods as well as alcohol and tobacco usage.
Learn more about recovery methods for athletes.
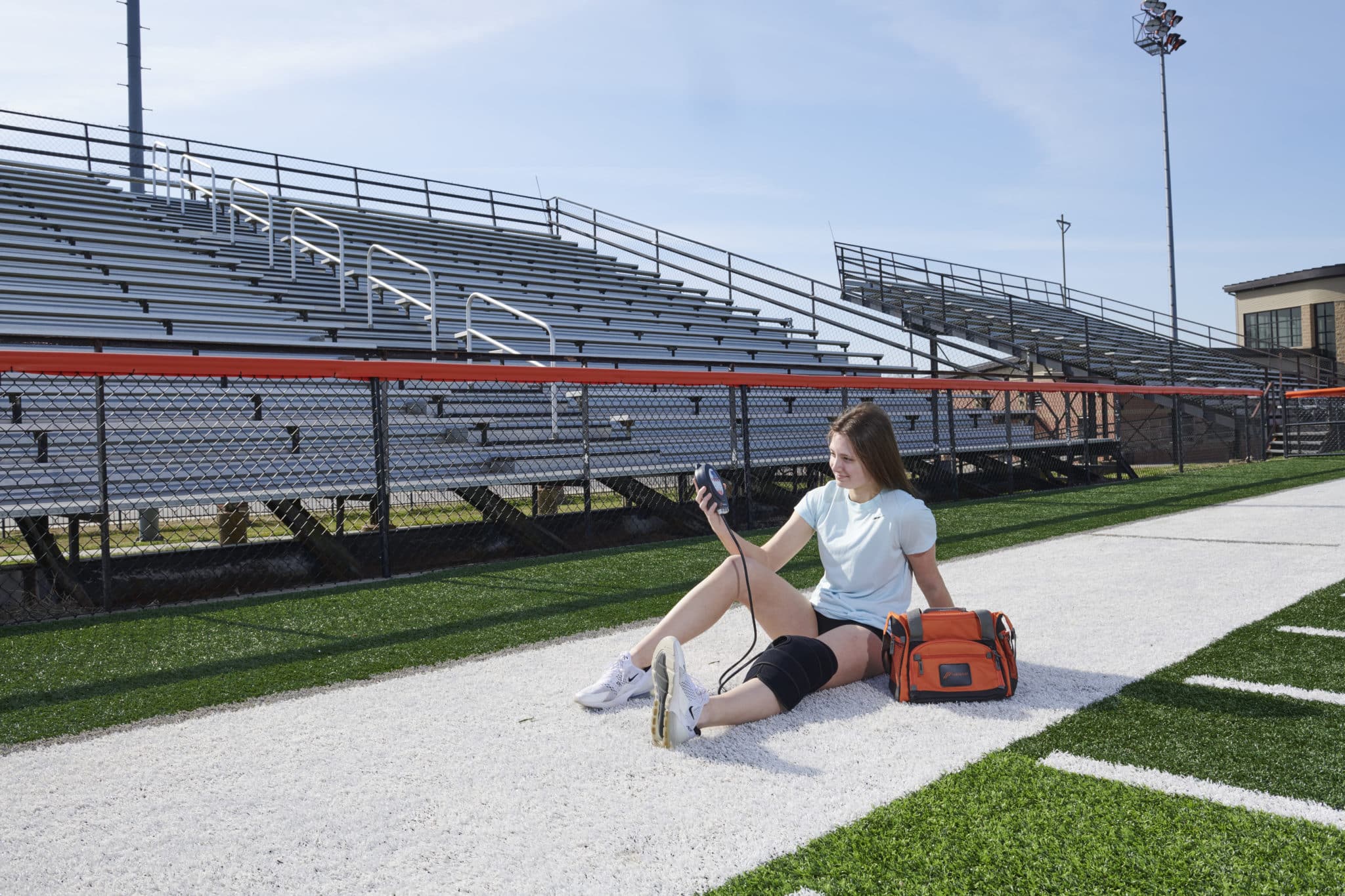
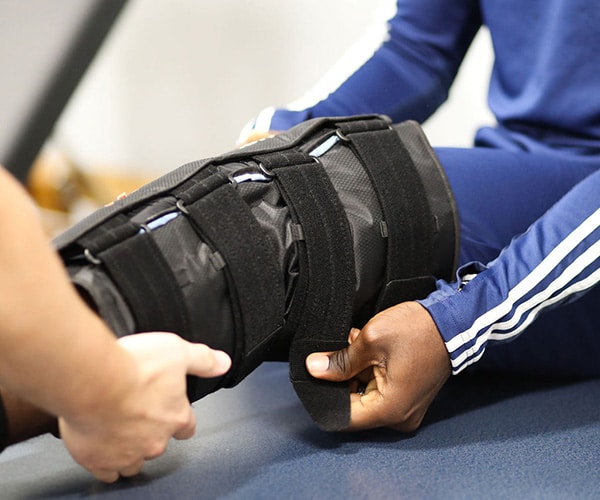
Leg Compression Therapy
Even with hydration and eating a well balanced diet, lactic acid buildup is common after an intense workout. Leg pain and tingling is caused by lactic acid buildup and muscle fatigue.
One way to combat the pain and discomfort associated with lactic acid buildup is to apply leg compression therapy. However, by participating in leg compression therapy for a half hour after a workout, many athletes can begin to feel a difference.
When it comes to compression devices, athletes have so many options. There are compression socks, which are typically made for long-term wear. You can also utilize full leg compression sleeves that provide coverage from the foot all the way up the leg.

Cold Compression Therapy for Athletes: Level Up Your Game
Rest and recovery are crucial to staying healthy and performing well as an athlete. Adding cold and compression therapy to a well-rounded fitness and health routine will likely help athletes improve their performance even further.
To level up your performance, make sure to stay up-to-date with the latest news and tips for incorporating cold compression therapy into your regimen by signing up for our newsletter.