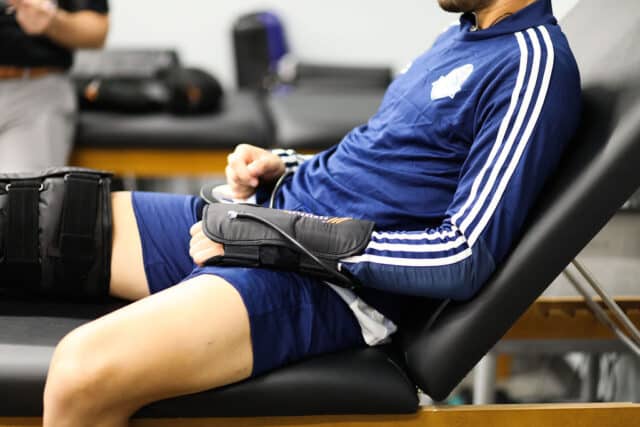
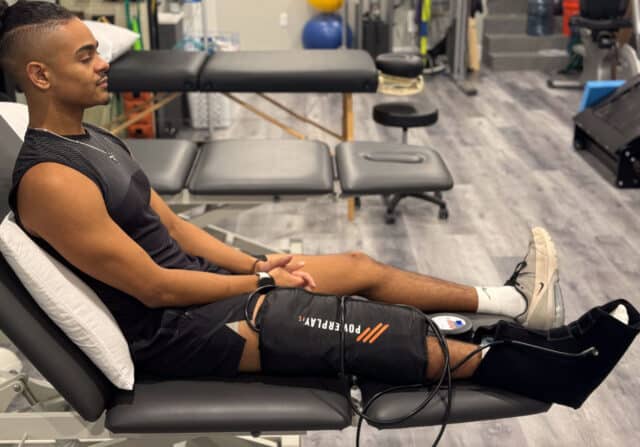
When it comes to recovery, pain and inflammation can stand in the way of returning to health and performance.
Dan MacLean earned his Masters of Physical Therapy from Sacramento State University and has been treating pain and inflammation for over a decade in a variety of contexts. Today, he is a sports physical therapist and owner of MAC Performance Physical Therapy in California.
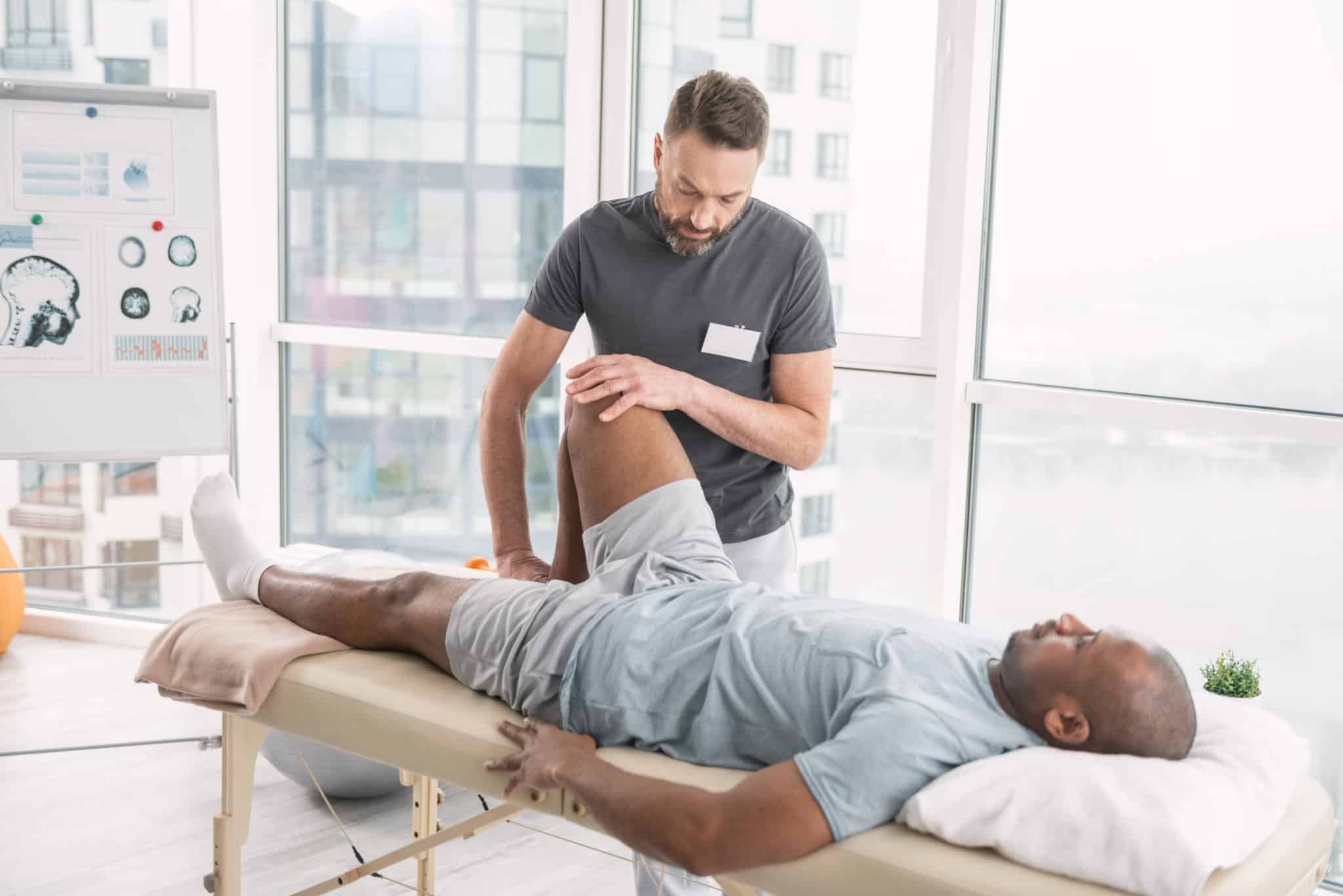
“Performance-based physical therapy is looking to get people back to performance. Physical therapy often aims to get people out of pain, but there’s a lot more in the rehab process to get people back to performing at a higher level, whether that’s hiking, running, or playing sports.”
Dan MacLean, MPT
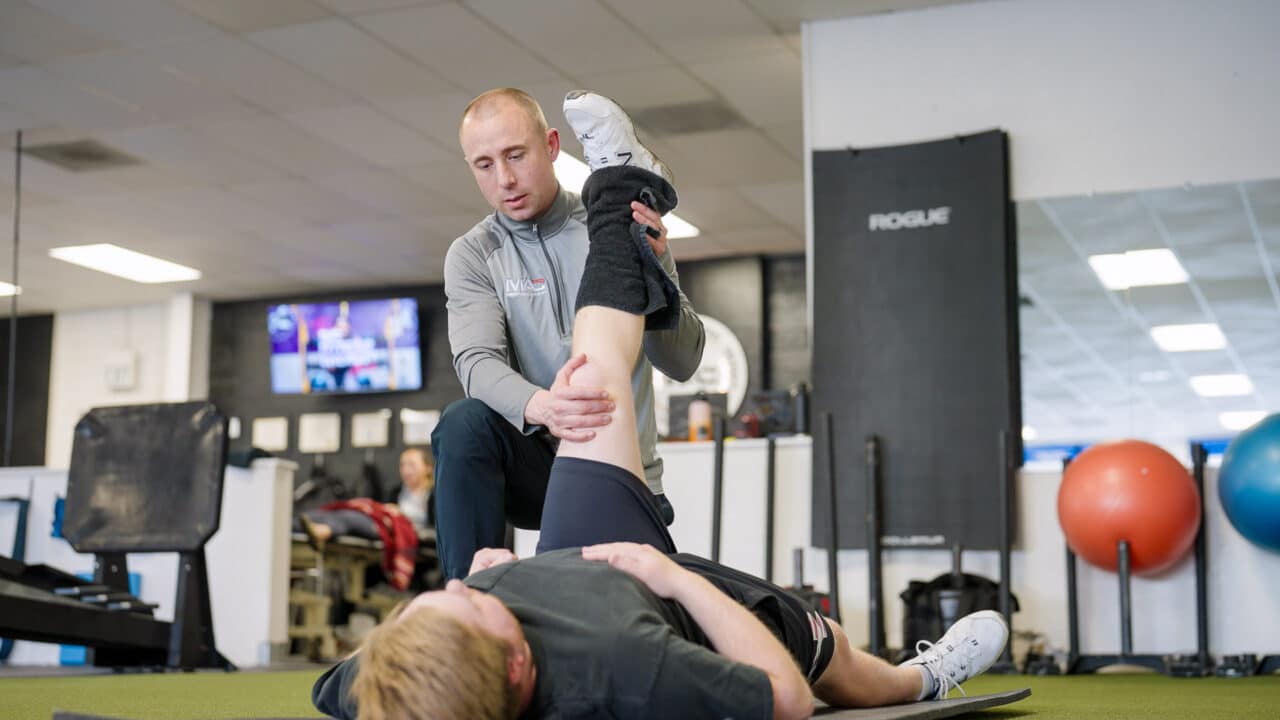

Using Cold Compression for Pain and Inflammation
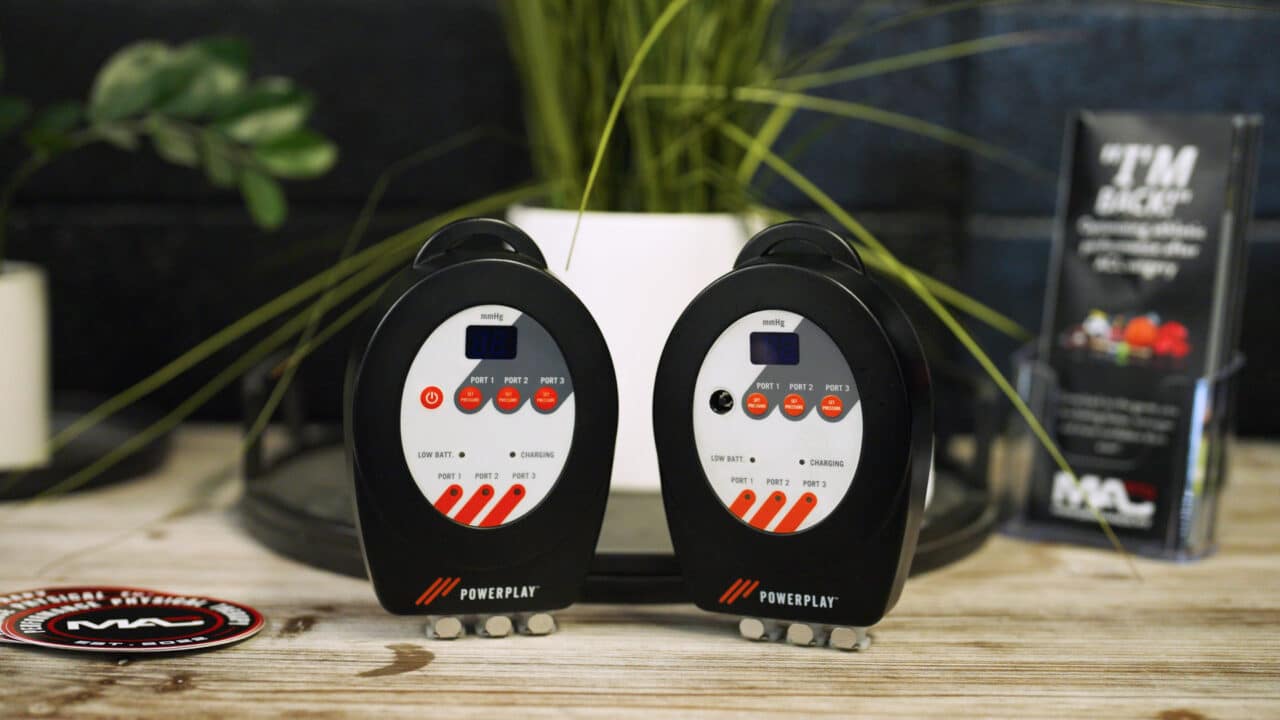
Dan and his team frequently incorporate the PowerPlay cold compression system into their physical therapy program. This cutting-edge technology has proven to be a game-changer in addressing pain and inflammation, the primary concerns that lead patients to seek physical therapy.
Dan explains that pain can arise from mechanical problems like tears or joint issues, inflammation putting pressure on nerves, or even psychological factors.
Cold therapy is an effective treatment for alleviating pain.
“We typically have people with chronic pain utilize cold therapy three to four times a day for 15 to 20 minutes at a time. That can really help offset their pain throughout the day,” Dan says.
Reducing Inflammation with Compression Therapy
While some inflammation is a natural part of the healing process, uncontrolled inflammation can impede recovery. That’s where the compression therapy can help.
“PowerPlay units do intermittent compression, squeezing and relaxing several times through a cycle. We’ve seen great effects in reducing chronic inflammation, which can also reduce pain.” Dan MacLean, PT, DPT
Dan notes that inflammation often arises when people are in static positions for a period of time and then try to move. Monitoring morning stiffness and soreness, as well as comparing joint measurements to the opposite limb, helps track progress in the inflammatory phase.
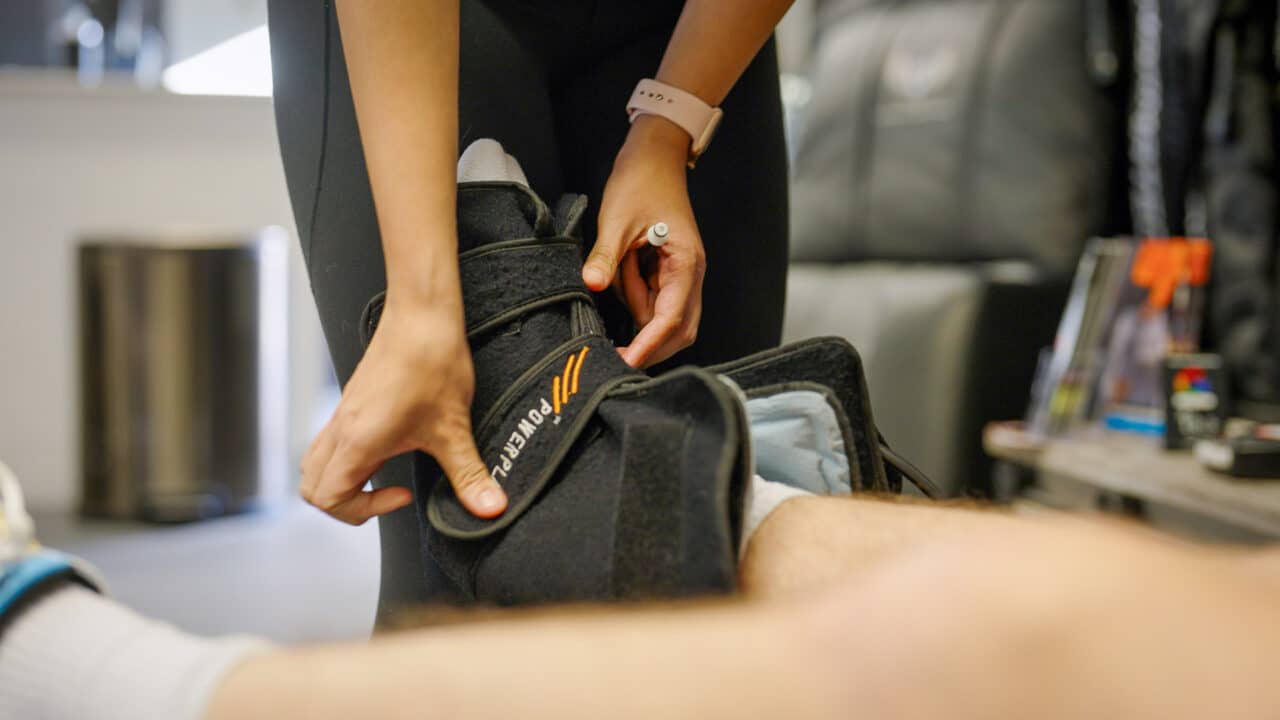

Benefits of Combining Cold and Compression
The PowerPlay system is ideal for patients experiencing both pain and inflammation because the cold helps with pain while the compression helps with inflammation.
“The ability for PowerPlay to do both cold and compression at the same time is a huge benefit,” Dan says. “You’re addressing not only the short-term pain someone is experiencing but also potentially longer-term pain from inflammation putting pressure on structures around the joints.”
At MAC Performance PT, physical therapists use PowerPlay to treat a variety of conditions, including post-surgical recovery from ACL and Achilles surgeries, rotator cuff repairs, and more.
Many patients will finish treatment sessions with PowerPlay, and some even decide to purchase a unit for home use, especially in the first weeks after surgery when pain and inflammation are most problematic.
“We’ve seen people who utilize the device at home after surgery are typically more comfortable, can perform their exercises better, and hopefully don’t have to use as much pain medication to supplement their recovery.”
Dan MacLean, MPT
Recover Better with PowerPlay
While there are many cold therapy options like ice packs, gel packs, and cold whirlpools, Dan highlights several benefits of PowerPlay:
- Combines cold and compression
- Simple and easy for patients to use
- Quick and accessible without getting wet
- Gel packs return to frozen state rapidly
He encourages anyone dealing with pain and inflammation to contact their local healthcare provider for guidance. PowerPlay cold compression therapy could be a valuable addition to help you recover better and get back to the activities you love.
Explore PowerPlay’s complete catalog of cold-compression wraps and pumps.

This post was originally published on April 29, 2024.
*The information featured on this page is subject to our standard content policy and disclaimer. It is available for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice.